7.3、数据格式化
在如Web /客户端项目中,通常需要将数据转换为具有某种格式的字符串进行展示,因此上节我们学习的数据类型转换系统核心作用不是完成这个需求,因此Spring3引入了格式化转换器(Formatter SPI) 和格式化服务API(FormattingConversionService)从而支持这种需求。在Spring中它和PropertyEditor功能类似,可以替代PropertyEditor来进行对象的解析和格式化,而且支持细粒度的字段级别的格式化/解析。
Formatter SPI核心是完成解析和格式化转换逻辑,在如Web应用/客户端项目中,需要解析、打印/展示本地化的对象值时使用,如根据Locale信息将java.util.Date---->java.lang.String打印/展示、java.lang.String---->java.util.Date等。
该格式化转换系统是Spring通用的,其定义在org.springframework.format包中,不仅仅在Spring Web MVC场景下。
7.3.1、架构
1、格式化转换器:提供格式化转换的实现支持。
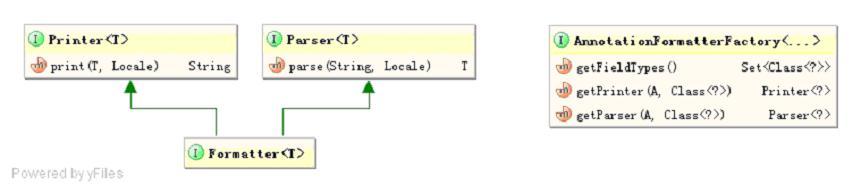
一共有如下两组四个接口:
(1、Printer接口:格式化显示接口,将T类型的对象根据Locale信息以某种格式进行打印显示(即返回字符串形式);
- package org.springframework.format;
- public interface Printer<T> {
- String print(T object, Locale locale);
- }
package org.springframework.format;
public interface Printer<T> {
String print(T object, Locale locale);
}
(2、Parser接口:解析接口,根据Locale信息解析字符串到T类型的对象;
- package org.springframework.format;
- public interface Parser<T> {
- T parse(String text, Locale locale) throws ParseException;
- }
package org.springframework.format;
public interface Parser<T> {
T parse(String text, Locale locale) throws ParseException;
}
解析失败可以抛出java.text.ParseException或IllegalArgumentException异常即可。
(3、Formatter接口:格式化SPI接口,继承Printer和Parser接口,完成T类型对象的格式化和解析功能;
- package org.springframework.format;
- public interface Formatter<T> extends Printer<T>, Parser<T> {
- }
package org.springframework.format;
public interface Formatter<T> extends Printer<T>, Parser<T> {
}
(4、AnnotationFormatterFactory接口:注解驱动的字段格式化工厂,用于创建带注解的对象字段的Printer和Parser,即用于格式化和解析带注解的对象字段。
- package org.springframework.format;
- public interface AnnotationFormatterFactory<A extends Annotation> {//①可以识别的注解类型
- Set<Class<?>> getFieldTypes();//②可以被A注解类型注解的字段类型集合
- Printer<?> getPrinter(A annotation, Class<?> fieldType);//③根据A注解类型和fieldType类型获取Printer
- Parser<?> getParser(A annotation, Class<?> fieldType);//④根据A注解类型和fieldType类型获取Parser
- }
package org.springframework.format;
public interface AnnotationFormatterFactory<A extends Annotation> {//①可以识别的注解类型
Set<Class<?>> getFieldTypes();//②可以被A注解类型注解的字段类型集合
Printer<?> getPrinter(A annotation, Class<?> fieldType);//③根据A注解类型和fieldType类型获取Printer
Parser<?> getParser(A annotation, Class<?> fieldType);//④根据A注解类型和fieldType类型获取Parser
}
返回用于格式化和解析被A注解类型注解的字段值的Printer和Parser。如JodaDateTimeFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory可以为带有@DateTimeFormat注解的java.util.Date字段类型创建相应的Printer和Parser进行格式化和解析。
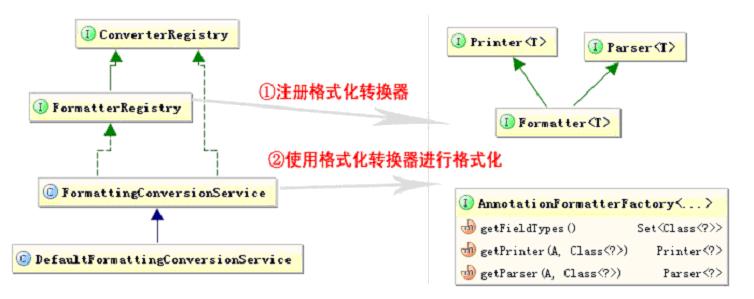
2、格式化转换器注册器、格式化服务:提供类型转换器注册支持,运行时类型转换API支持。
一个有如下两种接口:
(1、FormatterRegistry:格式化转换器注册器,用于注册格式化转换器(Formatter、Printer和Parser、AnnotationFormatterFactory);
- package org.springframework.format;
- public interface FormatterRegistry extends ConverterRegistry {
- //①添加格式化转换器(Spring3.1 新增API)
- void addFormatter(Formatter<?> formatter);
- //②为指定的字段类型添加格式化转换器
- void addFormatterForFieldType(Class<?> fieldType, Formatter<?> formatter);
- //③为指定的字段类型添加Printer和Parser
- void addFormatterForFieldType(Class<?> fieldType, Printer<?> printer, Parser<?> parser);
- //④添加注解驱动的字段格式化工厂AnnotationFormatterFactory
- void addFormatterForFieldAnnotation(
- AnnotationFormatterFactory<? extends Annotation> annotationFormatterFactory);
- }
package org.springframework.format;
public interface FormatterRegistry extends ConverterRegistry {
//①添加格式化转换器(Spring3.1 新增API)
void addFormatter(Formatter<?> formatter);
//②为指定的字段类型添加格式化转换器
void addFormatterForFieldType(Class<?> fieldType, Formatter<?> formatter);
//③为指定的字段类型添加Printer和Parser
void addFormatterForFieldType(Class<?> fieldType, Printer<?> printer, Parser<?> parser);
//④添加注解驱动的字段格式化工厂AnnotationFormatterFactory
void addFormatterForFieldAnnotation(
AnnotationFormatterFactory<? extends Annotation> annotationFormatterFactory);
}
(2、FormattingConversionService:继承自ConversionService,运行时类型转换和格式化服务接口,提供运行期类型转换和格式化的支持。
FormattingConversionService内部实现如下图所示:

我们可以看到FormattingConversionService内部实现如上所示,当你调用convert方法时:
⑴若是S类型----->String:调用私有的静态内部类PrinterConverter,其又调用相应的Printer的实现进行格式化;
⑵若是String----->T类型:调用私有的静态内部类ParserConverter,其又调用相应的Parser的实现进行解析;
⑶若是A注解类型注解的S类型----->String:调用私有的静态内部类AnnotationPrinterConverter,其又调用相应的AnnotationFormatterFactory的getPrinter获取Printer的实现进行格式化;
⑷若是String----->A注解类型注解的T类型:调用私有的静态内部类AnnotationParserConverter,其又调用相应的AnnotationFormatterFactory的getParser获取Parser的实现进行解析。
注:S类型表示源类型,T类型表示目标类型,A表示注解类型。
此处可以可以看出之前的Converter SPI完成任意Object与Object之间的类型转换,而Formatter SPI完成任意Object与String之间的类型转换(即格式化和解析,与PropertyEditor类似)。
7.3.2、Spring内建的格式化转换器如下所示:
|
类名
|
说明
|
|
DateFormatter
|
java.util.Date<---->String
实现日期的格式化/解析
|
|
NumberFormatter
|
java.lang.Number<---->String
实现通用样式的格式化/解析
|
|
CurrencyFormatter
|
java.lang.BigDecimal<---->String
实现货币样式的格式化/解析
|
|
PercentFormatter
|
java.lang.Number<---->String
实现百分数样式的格式化/解析
|
|
NumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory
|
@NumberFormat注解类型的数字字段类型<---->String
①通过@NumberFormat指定格式化/解析格式
②可以格式化/解析的数字类型:Short、Integer、Long、Float、Double、BigDecimal、BigInteger
|
|
JodaDateTimeFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory
|
@DateTimeFormat注解类型的日期字段类型<---->String
①通过@DateTimeFormat指定格式化/解析格式
②可以格式化/解析的日期类型:
joda中的日期类型(org.joda.time包中的):LocalDate、LocalDateTime、LocalTime、ReadableInstant
java内置的日期类型:Date、Calendar、Long
classpath中必须有Joda-Time类库,否则无法格式化日期类型
|
NumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory和JodaDateTimeFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory(如果classpath提供了Joda-Time类库)在使用格式化服务实现DefaultFormattingConversionService时会自动注册。
7.3.3、示例
在示例之前,我们需要到http://joda-time.sourceforge.net/下载Joda-Time类库,本书使用的是joda-time-2.1版本,将如下jar包添加到classpath:
joda-time-2.1.jar
7.3.3.1、类型级别的解析/格式化
一、直接使用Formatter SPI进行解析/格式化
- //二、CurrencyFormatter:实现货币样式的格式化/解析
- CurrencyFormatter currencyFormatter = new CurrencyFormatter();
- currencyFormatter.setFractionDigits(2);//保留小数点后几位
- currencyFormatter.setRoundingMode(RoundingMode.CEILING);//舍入模式(ceilling表示四舍五入)
- //1、将带货币符号的字符串“$123.125”转换为BigDecimal("123.00")
- Assert.assertEquals(new BigDecimal("123.13"), currencyFormatter.parse("$123.125", Locale.US));
- //2、将BigDecimal("123")格式化为字符串“$123.00”展示
- Assert.assertEquals("$123.00", currencyFormatter.print(new BigDecimal("123"), Locale.US));
- Assert.assertEquals("¥123.00", currencyFormatter.print(new BigDecimal("123"), Locale.CHINA));
- Assert.assertEquals("¥123.00", currencyFormatter.print(new BigDecimal("123"), Locale.JAPAN));
//二、CurrencyFormatter:实现货币样式的格式化/解析
CurrencyFormatter currencyFormatter = new CurrencyFormatter();
currencyFormatter.setFractionDigits(2);//保留小数点后几位
currencyFormatter.setRoundingMode(RoundingMode.CEILING);//舍入模式(ceilling表示四舍五入)
//1、将带货币符号的字符串“$123.125”转换为BigDecimal("123.00")
Assert.assertEquals(new BigDecimal("123.13"), currencyFormatter.parse("$123.125", Locale.US));
//2、将BigDecimal("123")格式化为字符串“$123.00”展示
Assert.assertEquals("$123.00", currencyFormatter.print(new BigDecimal("123"), Locale.US));
Assert.assertEquals("¥123.00", currencyFormatter.print(new BigDecimal("123"), Locale.CHINA));
Assert.assertEquals("¥123.00", currencyFormatter.print(new BigDecimal("123"), Locale.JAPAN));
parse方法:将带格式的字符串根据Locale信息解析为相应的BigDecimal类型数据;
print方法:将BigDecimal类型数据根据Locale信息格式化为字符串数据进行展示。
不同于Convert SPI,Formatter SPI可以根据本地化(Locale)信息进行解析/格式化。
其他测试用例请参考cn.javass.chapter7.web.controller.support.formatter.InnerFormatterTest的testNumber测试方法和testDate测试方法。
- @Test
- public void testWithDefaultFormattingConversionService() {
- DefaultFormattingConversionService conversionService = new DefaultFormattingConversionService();
- //默认不自动注册任何Formatter
- CurrencyFormatter currencyFormatter = new CurrencyFormatter();
- currencyFormatter.setFractionDigits(2);//保留小数点后几位
- currencyFormatter.setRoundingMode(RoundingMode.CEILING);//舍入模式(ceilling表示四舍五入)
- //注册Formatter SPI实现
- conversionService.addFormatter(currencyFormatter);
- //绑定Locale信息到ThreadLocal
- //FormattingConversionService内部自动获取作为Locale信息,如果不设值默认是 Locale.getDefault()
- LocaleContextHolder.setLocale(Locale.US);
- Assert.assertEquals("$1,234.13", conversionService.convert(new BigDecimal("1234.128"), String.class));
- LocaleContextHolder.setLocale(null);
- LocaleContextHolder.setLocale(Locale.CHINA);
- Assert.assertEquals("¥1,234.13", conversionService.convert(new BigDecimal("1234.128"), String.class));
- Assert.assertEquals(new BigDecimal("1234.13"), conversionService.convert("¥1,234.13", BigDecimal.class));
- LocaleContextHolder.setLocale(null);}
@Test
public void testWithDefaultFormattingConversionService() {
DefaultFormattingConversionService conversionService = new DefaultFormattingConversionService();
//默认不自动注册任何Formatter
CurrencyFormatter currencyFormatter = new CurrencyFormatter();
currencyFormatter.setFractionDigits(2);//保留小数点后几位
currencyFormatter.setRoundingMode(RoundingMode.CEILING);//舍入模式(ceilling表示四舍五入)
//注册Formatter SPI实现
conversionService.addFormatter(currencyFormatter);
//绑定Locale信息到ThreadLocal
//FormattingConversionService内部自动获取作为Locale信息,如果不设值默认是 Locale.getDefault()
LocaleContextHolder.setLocale(Locale.US);
Assert.assertEquals("$1,234.13", conversionService.convert(new BigDecimal("1234.128"), String.class));
LocaleContextHolder.setLocale(null);
LocaleContextHolder.setLocale(Locale.CHINA);
Assert.assertEquals("¥1,234.13", conversionService.convert(new BigDecimal("1234.128"), String.class));
Assert.assertEquals(new BigDecimal("1234.13"), conversionService.convert("¥1,234.13", BigDecimal.class));
LocaleContextHolder.setLocale(null);}
DefaultFormattingConversionService:带数据格式化功能的类型转换服务实现;
conversionService.addFormatter():注册Formatter SPI实现;
conversionService.convert(new BigDecimal("1234.128"), String.class):用于将BigDecimal类型数据格式化为字符串类型,此处根据“LocaleContextHolder.setLocale(locale)”设置的本地化信息进行格式化;
conversionService.convert("¥1,234.13", BigDecimal.class):用于将字符串类型数据解析为BigDecimal类型数据,此处也是根据“LocaleContextHolder.setLocale(locale)”设置的本地化信息进行解;
LocaleContextHolder.setLocale(locale):设置本地化信息到ThreadLocal,以便Formatter SPI根据本地化信息进行解析/格式化;
具体测试代码请参考cn.javass.chapter7.web.controller.support.formatter.InnerFormatterTest的testWithDefaultFormattingConversionService测试方法。
三、自定义Formatter进行解析/格式化
此处以解析/格式化PhoneNumberModel为例。
(1、定义Formatter SPI实现
- package cn.javass.chapter7.web.controller.support.formatter;
- //省略import
- public class PhoneNumberFormatter implements Formatter<PhoneNumberModel> {
- Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("^(\\d{3,4})-(\\d{7,8})$");
- @Override
- public String print(PhoneNumberModel phoneNumber, Locale locale) {//①格式化
- if(phoneNumber == null) {
- return "";
- }
- return new StringBuilder().append(phoneNumber.getAreaCode()).append("-")
- .append(phoneNumber.getPhoneNumber()).toString();
- }
- @Override
- public PhoneNumberModel parse(String text, Locale locale) throws ParseException {//②解析
- if(!StringUtils.hasLength(text)) {
- //①如果source为空 返回null
- return null;
- }
- Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(text);
- if(matcher.matches()) {
- //②如果匹配 进行转换
- PhoneNumberModel phoneNumber = new PhoneNumberModel();
- phoneNumber.setAreaCode(matcher.group(1));
- phoneNumber.setPhoneNumber(matcher.group(2));
- return phoneNumber;
- } else {
- //③如果不匹配 转换失败
- throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("类型转换失败,需要格式[010-12345678],但格式是[%s]", text));
- }
- }
- }
package cn.javass.chapter7.web.controller.support.formatter;
//省略import
public class PhoneNumberFormatter implements Formatter<PhoneNumberModel> {
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("^(\\d{3,4})-(\\d{7,8})___FCKpd___8quot;);
@Override
public String print(PhoneNumberModel phoneNumber, Locale locale) {//①格式化
if(phoneNumber == null) {
return "";
}
return new StringBuilder().append(phoneNumber.getAreaCode()).append("-")
.append(phoneNumber.getPhoneNumber()).toString();
}
@Override
public PhoneNumberModel parse(String text, Locale locale) throws ParseException {//②解析
if(!StringUtils.hasLength(text)) {
//①如果source为空 返回null
return null;
}
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(text);
if(matcher.matches()) {
//②如果匹配 进行转换
PhoneNumberModel phoneNumber = new PhoneNumberModel();
phoneNumber.setAreaCode(matcher.group(1));
phoneNumber.setPhoneNumber(matcher.group(2));
return phoneNumber;
} else {
//③如果不匹配 转换失败
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("类型转换失败,需要格式[010-12345678],但格式是[%s]", text));
}
}
}
类似于Convert SPI实现,只是此处的相应方法会传入Locale本地化信息,这样可以为不同地区进行解析/格式化数据。
(2、测试用例:
- package cn.javass.chapter7.web.controller.support.formatter;
- //省略import
- public class CustomerFormatterTest {
- @Test
- public void test() {
- DefaultFormattingConversionService conversionService = new DefaultFormattingConversionService();
- conversionService.addFormatter(new PhoneNumberFormatter());
- PhoneNumberModel phoneNumber = new PhoneNumberModel("010", "12345678");
- Assert.assertEquals("010-12345678", conversionService.convert(phoneNumber, String.class));
- Assert.assertEquals("010", conversionService.convert("010-12345678", PhoneNumberModel.class).getAreaCode());
- }
- }
package cn.javass.chapter7.web.controller.support.formatter;
//省略import
public class CustomerFormatterTest {
@Test
public void test() {
DefaultFormattingConversionService conversionService = new DefaultFormattingConversionService();
conversionService.addFormatter(new PhoneNumberFormatter());
PhoneNumberModel phoneNumber = new PhoneNumberModel("010", "12345678");
Assert.assertEquals("010-12345678", conversionService.convert(phoneNumber, String.class));
Assert.assertEquals("010", conversionService.convert("010-12345678", PhoneNumberModel.class).getAreaCode());
}
}
通过PhoneNumberFormatter可以解析String--->PhoneNumberModel和格式化PhoneNumberModel--->String。
到此,类型级别的解析/格式化我们就介绍完了,从测试用例可以看出类型级别的是对项目中的整个类型实施相同的解析/格式化逻辑。
有的同学可能需要在不同的类的字段实施不同的解析/格式化逻辑,如用户模型类的注册日期字段只需要如“2012-05-02”格式进行解析/格式化即可,而订单模型类的下订单日期字段可能需要如“2012-05-02 20:13:13”格式进行展示。
接下来我们学习一下如何进行字段级别的解析/格式化吧。
7.3.3.2、字段级别的解析/格式化
一、使用内置的注解进行字段级别的解析/格式化:
(1、测试模型类准备:
- package cn.javass.chapter7.model;
- public class FormatterModel {
- @NumberFormat(style=Style.NUMBER, pattern="#,###")
- private int totalCount;
- @NumberFormat(style=Style.PERCENT)
- private double discount;
- @NumberFormat(style=Style.CURRENCY)
- private double sumMoney;
- @DateTimeFormat(iso=ISO.DATE)
- private Date registerDate;
- @DateTimeFormat(pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
- private Date orderDate;
- //省略getter/setter
- }
package cn.javass.chapter7.model;
public class FormatterModel {
@NumberFormat(style=Style.NUMBER, pattern="#,###")
private int totalCount;
@NumberFormat(style=Style.PERCENT)
private double discount;
@NumberFormat(style=Style.CURRENCY)
private double sumMoney;
@DateTimeFormat(iso=ISO.DATE)
private Date registerDate;
@DateTimeFormat(pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
private Date orderDate;
//省略getter/setter
}
此处我们使用了Spring字段级别解析/格式化的两个内置注解:
@Number:定义数字相关的解析/格式化元数据(通用样式、货币样式、百分数样式),参数如下:
style:用于指定样式类型,包括三种:Style.NUMBER(通用样式) Style.CURRENCY(货币样式) Style.PERCENT(百分数样式),默认Style.NUMBER;
pattern:自定义样式,如patter="#,###";
@DateTimeFormat:定义日期相关的解析/格式化元数据,参数如下:
pattern:指定解析/格式化字段数据的模式,如”yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss”
iso:指定解析/格式化字段数据的ISO模式,包括四种:ISO.NONE(不使用) ISO.DATE(yyyy-MM-dd) ISO.TIME(hh:mm:ss.SSSZ) ISO.DATE_TIME(yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss.SSSZ),默认ISO.NONE;
style:指定用于格式化的样式模式,默认“SS”,具体使用请参考Joda-Time类库的org.joda.time.format.DateTimeFormat的forStyle的javadoc;
优先级: pattern 大于 iso 大于 style。
(2、测试用例:
- @Test
- public void test() throws SecurityException, NoSuchFieldException {
- //默认自动注册对@NumberFormat和@DateTimeFormat的支持
- DefaultFormattingConversionService conversionService =
- new DefaultFormattingConversionService();
- //准备测试模型对象
- FormatterModel model = new FormatterModel();
- model.setTotalCount(10000);
- model.setDiscount(0.51);
- model.setSumMoney(10000.13);
- model.setRegisterDate(new Date(2012-1900, 4, 1));
- model.setOrderDate(new Date(2012-1900, 4, 1, 20, 18, 18));
- //获取类型信息
- TypeDescriptor descriptor =
- new TypeDescriptor(FormatterModel.class.getDeclaredField("totalCount"));
- TypeDescriptor stringDescriptor = TypeDescriptor.valueOf(String.class);
- Assert.assertEquals("10,000", conversionService.convert(model.getTotalCount(), descriptor, stringDescriptor));
- Assert.assertEquals(model.getTotalCount(), conversionService.convert("10,000", stringDescriptor, descriptor));
- }
@Test
public void test() throws SecurityException, NoSuchFieldException {
//默认自动注册对@NumberFormat和@DateTimeFormat的支持
DefaultFormattingConversionService conversionService =
new DefaultFormattingConversionService();
//准备测试模型对象
FormatterModel model = new FormatterModel();
model.setTotalCount(10000);
model.setDiscount(0.51);
model.setSumMoney(10000.13);
model.setRegisterDate(new Date(2012-1900, 4, 1));
model.setOrderDate(new Date(2012-1900, 4, 1, 20, 18, 18));
//获取类型信息
TypeDescriptor descriptor =
new TypeDescriptor(FormatterModel.class.getDeclaredField("totalCount"));
TypeDescriptor stringDescriptor = TypeDescriptor.valueOf(String.class);
Assert.assertEquals("10,000", conversionService.convert(model.getTotalCount(), descriptor, stringDescriptor));
Assert.assertEquals(model.getTotalCount(), conversionService.convert("10,000", stringDescriptor, descriptor));
}
TypeDescriptor:拥有类型信息的上下文,用于Spring3类型转换系统获取类型信息的(可以包含类、字段、方法参数、属性信息);通过TypeDescriptor,我们就可以获取(类、字段、方法参数、属性)的各种信息,如注解类型信息;
conversionService.convert(model.getTotalCount(), descriptor, stringDescriptor):将totalCount格式化为字符串类型,此处会根据totalCount字段的注解信息(通过descriptor对象获取)来进行格式化;
conversionService.convert("10,000", stringDescriptor, descriptor):将字符串“10,000”解析为totalCount字段类型,此处会根据totalCount字段的注解信息(通过descriptor对象获取)来进行解析。
(3、通过为不同的字段指定不同的注解信息进行字段级别的细粒度数据解析/格式化
- descriptor = new TypeDescriptor(FormatterModel.class.getDeclaredField("registerDate"));
- Assert.assertEquals("2012-05-01", conversionService.convert(model.getRegisterDate(), descriptor, stringDescriptor));
- Assert.assertEquals(model.getRegisterDate(), conversionService.convert("2012-05-01", stringDescriptor, descriptor));
- descriptor = new TypeDescriptor(FormatterModel.class.getDeclaredField("orderDate"));
- Assert.assertEquals("2012-05-01 20:18:18", conversionService.convert(model.getOrderDate(), descriptor, stringDescriptor));
- Assert.assertEquals(model.getOrderDate(), conversionService.convert("2012-05-01 20:18:18", stringDescriptor, descriptor));
descriptor = new TypeDescriptor(FormatterModel.class.getDeclaredField("registerDate"));
Assert.assertEquals("2012-05-01", conversionService.convert(model.getRegisterDate(), descriptor, stringDescriptor));
Assert.assertEquals(model.getRegisterDate(), conversionService.convert("2012-05-01", stringDescriptor, descriptor));
descriptor = new TypeDescriptor(FormatterModel.class.getDeclaredField("orderDate"));
Assert.assertEquals("2012-05-01 20:18:18", conversionService.convert(model.getOrderDate(), descriptor, stringDescriptor));
Assert.assertEquals(model.getOrderDate(), conversionService.convert("2012-05-01 20:18:18", stringDescriptor, descriptor));
通过如上测试可以看出,我们可以通过字段注解方式实现细粒度的数据解析/格式化控制,但是必须使用TypeDescriptor来指定类型的上下文信息,即编程实现字段的数据解析/格式化比较麻烦。
其他测试用例请参考cn.javass.chapter7.web.controller.support.formatter.InnerFieldFormatterTest的test测试方法。
二、自定义注解进行字段级别的解析/格式化:
此处以解析/格式化PhoneNumberModel字段为例。
(1、定义解析/格式化字段的注解类型:
- package cn.javass.chapter7.web.controller.support.formatter;
- //省略import
- @Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.PARAMETER})
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
- public @interface PhoneNumber {
- }
package cn.javass.chapter7.web.controller.support.formatter;
//省略import
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface PhoneNumber {
}
(2、实现AnnotationFormatterFactory注解格式化工厂:
- package cn.javass.chapter7.web.controller.support.formatter;
- //省略import
- public class PhoneNumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory
- implements AnnotationFormatterFactory<PhoneNumber> {//①指定可以解析/格式化的字段注解类型
- private final Set<Class<?>> fieldTypes;
- private final PhoneNumberFormatter formatter;
- public PhoneNumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory() {
- Set<Class<?>> set = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
- set.add(PhoneNumberModel.class);
- this.fieldTypes = set;
- this.formatter = new PhoneNumberFormatter();//此处使用之前定义的Formatter实现
- }
- //②指定可以被解析/格式化的字段类型集合
- @Override
- public Set<Class<?>> getFieldTypes() {
- return fieldTypes;
- }
- //③根据注解信息和字段类型获取解析器
- @Override
- public Parser<?> getParser(PhoneNumber annotation, Class<?> fieldType) {
- return formatter;
- }
- //④根据注解信息和字段类型获取格式化器
- @Override
- public Printer<?> getPrinter(PhoneNumber annotation, Class<?> fieldType) {
- return formatter;
- }
- }
package cn.javass.chapter7.web.controller.support.formatter;
//省略import
public class PhoneNumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory
implements AnnotationFormatterFactory<PhoneNumber> {//①指定可以解析/格式化的字段注解类型
private final Set<Class<?>> fieldTypes;
private final PhoneNumberFormatter formatter;
public PhoneNumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory() {
Set<Class<?>> set = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
set.add(PhoneNumberModel.class);
this.fieldTypes = set;
this.formatter = new PhoneNumberFormatter();//此处使用之前定义的Formatter实现
}
//②指定可以被解析/格式化的字段类型集合
@Override
public Set<Class<?>> getFieldTypes() {
return fieldTypes;
}
//③根据注解信息和字段类型获取解析器
@Override
public Parser<?> getParser(PhoneNumber annotation, Class<?> fieldType) {
return formatter;
}
//④根据注解信息和字段类型获取格式化器
@Override
public Printer<?> getPrinter(PhoneNumber annotation, Class<?> fieldType) {
return formatter;
}
}
AnnotationFormatterFactory实现会根据注解信息和字段类型获取相应的解析器/格式化器。
(3、修改FormatterModel添加如下代码:
@PhoneNumber private PhoneNumberModel phoneNumber;
(4、测试用例
- @Test
- ublic void test() throws SecurityException, NoSuchFieldException {
- DefaultFormattingConversionService conversionService =
- new DefaultFormattingConversionService();//创建格式化服务
- conversionService.addFormatterForFieldAnnotation(
- new PhoneNumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory());//添加自定义的注解格式化工厂
- FormatterModel model = new FormatterModel();
- TypeDescriptor descriptor =
- new TypeDescriptor(FormatterModel.class.getDeclaredField("phoneNumber"));
- TypeDescriptor stringDescriptor = TypeDescriptor.valueOf(String.class);
- PhoneNumberModel value = (PhoneNumberModel) conversionService.convert("010-12345678", stringDescriptor, descriptor); //解析字符串"010-12345678"--> PhoneNumberModel
- model.setPhoneNumber(value);
- Assert.assertEquals("010-12345678", conversionService.convert(model.getPhoneNumber(), descriptor, stringDescriptor));//格式化PhoneNumberModel-->"010-12345678"
@Test
public void test() throws SecurityException, NoSuchFieldException {
DefaultFormattingConversionService conversionService =
new DefaultFormattingConversionService();//创建格式化服务
conversionService.addFormatterForFieldAnnotation(
new PhoneNumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory());//添加自定义的注解格式化工厂
FormatterModel model = new FormatterModel();
TypeDescriptor descriptor =
new TypeDescriptor(FormatterModel.class.getDeclaredField("phoneNumber"));
TypeDescriptor stringDescriptor = TypeDescriptor.valueOf(String.class);
PhoneNumberModel value = (PhoneNumberModel) conversionService.convert("010-12345678", stringDescriptor, descriptor); //解析字符串"010-12345678"--> PhoneNumberModel
model.setPhoneNumber(value);
Assert.assertEquals("010-12345678", conversionService.convert(model.getPhoneNumber(), descriptor, stringDescriptor));//格式化PhoneNumberModel-->"010-12345678"
}
此处使用DefaultFormattingConversionService的addFormatterForFieldAnnotation注册自定义的注解格式化工厂PhoneNumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory。
到此,编程进行数据的格式化/解析我们就完成了,使用起来还是比较麻烦,接下来我们将其集成到Spring Web MVC环境中。
7.3.4、集成到Spring Web MVC环境
一、注册FormattingConversionService实现和自定义格式化转换器:
- <bean id="conversionService"
- class="org.springframework.format.support.FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean">
- <!—此处省略之前注册的自定义类型转换器-->
- <property name="formatters">
- <list>
- <bean class="cn.javass.chapter7.web.controller.support.formatter.
- PhoneNumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory"/>
- </list>
- </property>
- </bean>
<bean id="conversionService"
class="org.springframework.format.support.FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<!—此处省略之前注册的自定义类型转换器-->
<property name="formatters">
<list>
<bean class="cn.javass.chapter7.web.controller.support.formatter.
PhoneNumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
其他配置和之前学习7.2.2.4一节一样。
二、示例:
(1、模型对象字段的数据解析/格式化:
- @RequestMapping(value = "/format1")
- public String test1(@ModelAttribute("model") FormatterModel formatModel) {
- return "format/success";
- }
@RequestMapping(value = "/format1")
public String test1(@ModelAttribute("model") FormatterModel formatModel) {
return "format/success";
}
- totalCount:<spring:bind path="model.totalCount">${status.value}</spring:bind><br/>
- discount:<spring:bind path="model.discount">${status.value}</spring:bind><br/>
- sumMoney:<spring:bind path="model.sumMoney">${status.value}</spring:bind><br/>
- phoneNumber:<spring:bind path="model.phoneNumber">${status.value}</spring:bind><br/>
- <!-- 如果没有配置org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.ConversionServiceExposingInterceptor将会报错 -->
- phoneNumber:<spring:eval expression="model.phoneNumber"></spring:eval><br/>
- <br/><br/>
- <form:form commandName="model">
- <form:input path="phoneNumber"/><br/>
- <form:input path="sumMoney"/>
- </form:form>
totalCount:<spring:bind path="model.totalCount">${status.value}</spring:bind><br/>
discount:<spring:bind path="model.discount">${status.value}</spring:bind><br/>
sumMoney:<spring:bind path="model.sumMoney">${status.value}</spring:bind><br/>
phoneNumber:<spring:bind path="model.phoneNumber">${status.value}</spring:bind><br/>
<!-- 如果没有配置org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.ConversionServiceExposingInterceptor将会报错 -->
phoneNumber:<spring:eval expression="model.phoneNumber"></spring:eval><br/>
<br/><br/>
<form:form commandName="model">
<form:input path="phoneNumber"/><br/>
<form:input path="sumMoney"/>
</form:form>
在浏览器输入测试URL:
http://localhost:9080/springmvc-chapter7/format1?totalCount=100000&discount=0.51&sumMoney=100000.128&phoneNumber=010-12345678
数据会正确绑定到我们的formatModel,即请求参数能被正确的解析并绑定到我们的命令对象上,而且在JSP页面也能正确的显示格式化后的数据(即正确的被格式化显示)。
(2、功能处理方法参数级别的数据解析:
- @RequestMapping(value = "/format2")
- public String test2(
- @PhoneNumber @RequestParam("phoneNumber") PhoneNumberModel phoneNumber,
- @DateTimeFormat(pattern="yyyy-MM-dd") @RequestParam("date") Date date) {
- System.out.println(phoneNumber);
- System.out.println(date);
- return "format/success2";
- }
@RequestMapping(value = "/format2")
public String test2(
@PhoneNumber @RequestParam("phoneNumber") PhoneNumberModel phoneNumber,
@DateTimeFormat(pattern="yyyy-MM-dd") @RequestParam("date") Date date) {
System.out.println(phoneNumber);
System.out.println(date);
return "format/success2";
}
此处我们可以直接在功能处理方法的参数上使用格式化注解类型进行注解,Spring Web MVC能根据此注解信息对请求参数进行解析并正确的绑定。
在浏览器输入测试URL:
http://localhost:9080/springmvc-chapter7/format2?phoneNumber=010-12345678&date=2012-05-01
数据会正确的绑定到我们的phoneNumber和date上,即请求的参数能被正确的解析并绑定到我们的参数上。
控制器代码位于cn.javass.chapter7.web.controller.DataFormatTestController中。
如果我们请求参数数据不能被正确解析并绑定或输入的数据不合法等该怎么处理呢?接下来的一节我们来学习下绑定失败处理和数据验证相关知识。
此文章由 http://www.ositren.com 收集整理 ,地址为: http://www.ositren.com/htmls/70071.html


